by Ted Strat
Climate change is the greatest challenge civilization has ever faced. As we tour through its causes, it becomes obvious that we have solutions. But climate change is complex and no single solution by itself will correct our predicament. The solutions integrate science and technology, energy and economics, moral and spiritual issues, plus government and politics. Besides, this is a global problem, created at the local level all the way up to a planetary scale.
The simple part of the solution is we have to stop using dirty fossil fuels. The burning of these fuels is responsible for our current warming. We should remember that greenhouse gases linger in the atmosphere for hundreds of years. The planet, particularly the oceans, requires time to respond to rising CO2 levels. Even if we stopped emitting greenhouse gases today, humanity is already on a path to some substantial level of climate warming into the future.
A big question is how much more disruption still lies “in the pipeline” and is coming our way? That will be determined by the extent to which society continues to use dirty fossil fuels – and how the global climate system responds to declining emissions. Despite increasing awareness of climate dangers, we still have to end the fossil fuel system. This has to end, and this is a major part of our challenge.
Solutions fit generally into two categories. We must reduce carbon emissions. In climate terminology, this is called “mitigation.” We also have to adapt to changing conditions and stabilize the atmosphere. This is called “adaptation.”
This compendium will present some of the most obvious solutions. We can solve this problem if we work together and recognize that major changes are ahead of us. The challenge is to apply these solutions – which also means changing how we live our lives.
A further breakdown of solutions gives us ten specific categories to address: (1) embrace clean renewable energy; (2) eliminate fossil fuel use; (3) boost energy efficiency; (4) shift to green forms of transportation; (5) protect the forests; (6) promote research and development of low-carbon technologies; (7) transform agriculture; (8) ensure sustainable development; (9) upgrade infrastructure, and (10) integrate human society into the ecosystem of the planet. If we can do these ten things, then humanity will survive and thrive. In this challenge, young people and their advocacy are critical. Besides young people have the most to gain, including all of their future and generations still to come.
Solar Power Is Clean And Renewable
Solar energy has the great potential “to reduce greenhouse gases and provide increased energy efficiency,” says a scientist at the U.S. Argonne National Laboratory, in a report published in the March, 2018 edition of Physics Today.
Solar energy provides this benefit because it captures the free energy in sunlight and uses it to replace dirty fossil fuel energy. To measure the value of solar power, across the U.S., about 29% of global warming emissions derive from electricity generation, most of which comes from coal and natural gas.
The benefits of solar power over fossil fuels becomes clear by examining the numbers. Burning natural gas for electricity releases between 0.6 and 2.0 pounds of CO2 equivalent per kilowatt-hour, and coal emits 1.4 to 3.6 pounds. In contrast, solar power emits 0.07 to 0.2; wind power provides only 0.02 to 0.04. Geothermal 0.1 to 0.2; and hydroelectric between 0.1 and 0.5. Even when including “life cycle” emissions (i.e., emissions from manufacturing, operation, installation, and decommissioning), the emissions associated with renewable energies are minimal. The differences are huge, not just in the greenhouse gas emissions, but also in the costs of production and the price to consumers.
Offshore Wind Could Power the Atlantic States
From Maine to Florida, the winds blowing off the Atlantic Coast could power a clean energy future, according to a 2018 report released by Environment America.
The key findings of this report show that winds blowing off the Atlantic coast could provide four times more electricity each year than the entire region currently uses, and 12 of the 14 coastal states have offshore wind potential that exceeds their current electricity consumption.
If these states converted all activities currently powered by gasoline, natural gas and other fossil fuels to electricity, the energy provided by offshore wind turbines could still produce at least twice as much power as they would use.
“We’re facing rising seas, intensifying storms, and old and new health threats because we’ve relied so long on dirty energy sources,” said Rob Sargent, energy director for Environment America. “But sitting right here next to us is the Atlantic Coast, and its winds provide a massive source of totally clean power. It’s about time for us to say, “Thank you, Mother Nature,” and do what we should have done in the first place, “Harness the wind.”
While offshore wind is a proven technology in other countries, it has been slow to take off in the United States. To date, only one offshore wind farm is operating in the U.S. Meanwhile, Europe hosts 4,100 offshore wind turbines that supply enough electricity to power more than 20 million homes each day. But more American offshore wind is waiting on the horizon.
The Bright Future Of Solar Power
Solar power is booming. Solar power is now cheaper than coal in most parts of the world, and generating power from the sun will become the lowest-cost energy option globally in less than ten years, says Bloomberg News. In many places around the world, solar is already the lowest-cost option.
Even big utility companies are moving rapidly into solar and wind power. In California Pacific Gas & Electric has committed to making clean, renewable energy, including solar, 55% of its power portfolio by 2031. Many experts believe that California will hit the 50% renewables mark by 2025, maybe sooner.
Compounding solar power’s impending energy dominance, researchers are exploring new ways to generate solar energy for human needs. Innovative methods of harnessing solar power, like stick-on solar tiles, solar windows and solar roof shingles, are coming soon to many communities.
New solar powered devices that can be transported with ease will allow for many new applications of sun power. Construction, camping, and industry will all benefit. Energy independent homes off the grid will become common. A goal will be to electrify everything and operate them with sun power.
Sun Powered Autos: Wave Of The Future
Electric vehicles could be cheaper than their gas-powered counterparts by 2025, if the price of new batteries continues its downward trajectory.
With many countries and companies already producing electric vehicles, greater deployment will drive down the price of lithium-ion batteries to as low as $70 per kilowatt hour (kwh) by 2030. The average 2018 price was $197 per kwh.
The number of cars and trucks in the U.S. is about 255 million vehicles in a nation of 321 million people. At the end of 2016, there were 542,000 all- electric vehicles on the road, a 641% growth over 2013. By early 2018 that number increased to over 750,000 vehicles. China already has 1.2 million EVs.
Electric vehicles are the wave of the future for several reasons: They are more efficient. They provide the owner with energy independence. They are less expensive to operate, especially if one has solar power. Sun power means zero emissions and zero impact on climate change. Already every automaker is racing to produce better electric vehicles. This is why the future of cars is solar.
The Huge Potential In Wave Power
Wave energy is unique because it is the most concentrated form of renewable energy on earth. It has a power density higher than either wind or solar energy. It is also more predictable and consistent than wind or solar. Ocean conditions can be accurately predicted 48 to 72 hours in advance, while accurate wind forecasts rarely are available more than 5 to 7 hours ahead.
In theory, ocean wave energy resource potential exceeds 50% of the annual domestic energy demand of the United States. It is located close to coastal population centers, and, although variable in nature, may be more consistent and predictable than some other renewable generation technologies. As a renewable electricity generation technology, ocean wave energy has a low air pollutant option and could help in diversifying the U.S. electricity generation portfolio.
With 71% of the earth’s surface covered by water, ocean waves represent the planet’s last great untapped natural renewable energy resource. Waves hold tremendous amounts of energy. We only need to tap into it.
White Walls Cool Warming Cities
These white buildings in Gaucin, Spain, cut heat by 4-5° F by reflecting the sunlight and heat away. It has long been known that white walls and roofs reduce the heat buildup in cities. New research affirms a traditional understanding that painting surfaces in light-reflecting colors can lower extreme temperatures in both big cities and small rural areas.
Summers in the city can be extremely hot — several degrees hotter than the surrounding countryside. But research shows that it does not have to be that way. The replacement of dark surfaces with white can lower heat wave temperatures in substantial amounts. With climate change and urbanization set to intensify “urban heat islands,” the case for such urban geoengineering to maintain our cool grows.
The phenomenon of the urban heat island has been understood since giant cities began to emerge in the 19th century. Generally, the darker the surface, the more heat it absorbs. Fresh asphalt reflects only 4% of sunlight compared to as much as 25% for grassland and up to 90% for a bright white surface such as fresh snow. Farmers can use this same principle by altering farming systems. Reducing local temperatures, for instance, decreases evaporation.
Light Grey Streets Reduce Urban Heat
Los Angeles has initiated a program to paint asphalt road surfaces with light gray paint to reduce road-top temperatures by as much as 10o F.
Keith Oleson from the National Center for Atmospheric Research in Boulder, Colorado, examined what might happen if every road and roof in large cities were painted white, increasing their reflectivity. This is known to climate scientists as “albedo.” Painting reflective coatings on roads and roofs would raise reflectivity from a typical 32% up to 90%. He found that this would decrease the urban heat island effect by over a third – enough to reduce maximum daytime temperatures by several degrees, and even more in hot areas.
It is well known that the urban heat island can be a killer. Recent research underlines that temperature peaks cause a spike in heart attacks. This is what happened during the European heat waves of 2003 and 2018 when tens of thousands of people died, mostly in homes without air conditioning. Doctors said the killer was not so much the 40-degree C daytime temperatures (104o F), but the fact that nights stayed at or above 30o C (86o F). Surprisingly the biggest effects of reflective painting are often at night. Vulnerable people, such as the old who are heat stressed during the day, need to cool down at night. Without that change, they can succumb to heat stroke and dehydration.
Plant Trees To Absorb Greenhouse Gases
On the eve of Independence Day, Pakistan launched a tree planting campaign in the coastal areas of Balochistan. The students above are participating in an effort to plant over one million saplings in the coastal region of Pakistan.
In every country, forests play an important role in climate change. The cutting and destruction of forests contributes to the release of CO2. But the planting of new forests mitigate against climate change by removing CO2 from the atmosphere. Combined with the sun’s energy, the captured carbon is converted into trunks, branches, roots and leaves via the photosynthesis process and oxygen is released. The carbon is stored in this green “biomass.”
Between now and 2050, restoring forests are one of our “most promising” tools. In a report, Oxford University researchers say that our best hopes are rather simple. They recommend two actions: Plant trees and improve the soil. Both techniques, said the report, will help the atmosphere no matter what. The two techniques it recommends are afforestation –
planting trees where there were none grew before –
and biochar – improving the soil by burying a layer
of dense charcoal.
Keep Fossil Fuels In The Ground
Physics has the ability to impose a sharp clarity on the often murky world of partisan politics. It can make things simple. Not necessarily easy, but simple.
In discussions about climate change, the basic controversy is simple: it’s short term financial gain over the long term health and welfare of the people. It’s corporate profits and investor fear of stranded financial assets versus the longterm health of the world, a stable climate and the predictable laws of physics.
Scientists know that burning fossil fuels – oil, coal, and gas – is driving the biggest challenge facing the world today: global climate change. Extreme weather events, rising seas, melting polar icecaps, acidifying oceans, record temperatures and droughts are the steady rise of greenhouse gases are wreaking havoc on hundreds of millions of lives and livelihoods around the world.
The simple conclusion is that we have to keep the remaining fossil-fuel reserves in the ground. If we don’t do this, if we dig up all the coal, oil and gas and burn them, we will overwhelm the planet’s physical systems, and heat the Earth beyond the red lines drawn by governments and scientists. This is the clear conclusion: “We have to keep it in the ground.”
Seaweed: A Nutritious Food Of The Future
Meet the women who are growing the new California seaweed economy. The state’s first open-ocean seaweed farm promises to become a solution to global food insecurity. Beyond the scenic beaches of Mendocino county, this is what could become the Golden State’s next big thing: seaweed as a new food source.
As climate change disrupts traditional agriculture, seaweed could become a major asset in the fight for sufficient food for the world. Seaweeds, really “sea vegetables,” readily absorb phosphorous, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide from the ocean, deacidifying the water and making it hospitable for marine species like shellfish. It is a protein-rich food that contains over 25 vitamins and more than 50 minerals. Plus seaweed shows excellent promise as a substitute for fossil fuels. Besides, seaweed grows rapidly and easily without fertilizer, without pesticides or help from external inputs.
With three distinct tiers of benefits, ocean farmer Catherine O’Hare calls seaweed a “win, win, win crop,” as it is a global solution to ocean acidification, unsustainable food systems, and climate change. She reports, “Sea greens are a true superfood. They contain more than 25 vitamins and over 50 minerals.”
New “Earthship” Housing Designs Are Ready
In the desert near Taos, New Mexico, a new biotectural design in off-the-grid home building is becoming popular. “Earthships” are passive solar homes. They use slanted panes of south facing glass to direct sunlight into the house and warm the internal space. More importantly, they are thermal mass homes.
Earthships are entirely self-sufficient. They use solar and wind power to generate all the electricity an average family will use. Every Earthship uses photovoltaic cells to store energy and supply the home. It generates all of its power and heat, collects its own water, and processes its waste. An Earthship recycles water, generates power, stabilizes temperatures, processes sewage and can even grow its own food.
Each Earthship is partially buried in the ground for extra insulation. The main framework is recycled tires filled with dirt. These tires absorb and hold the sun’s energy. Large glass windows for passive solar double as a greenhouse. Residents can even grow bananas and oranges in a cold northern region in the Rocky Mountains. The advantage of these homes is
that there are no adverse impacts on the surrounding land. They
are as near to zero in greenhouse gas emissions as possible. See
examples of these earthship home designs on the web.
Renewable Energy Is Growing Fast
The image above depicts a floating solar energy project in Huainan, China. In 2018 China installed as many solar panels as the entire solar capacity of France and Germany combined.
Around the world, renewable energy, including hydropower, wind and solar, was far and away the fastest-growing energy source. In 2017 new solar PV capacity grew by 50%, reaching over 74 gigawatts, with China accounting for almost half of this expansion. For the first time, photovoltaic (PV) additions rose faster than any other fuel, surpassing even the net growth in coal. And the prices for renewable energy technologies keep falling.
Solar PV is now entering a new era. Over the next five years, solar power will achieve its largest annual growth among renewables, well above wind and hydro. This increase underpins a more optimistic solar forecast which is revised up by over one-third compared to last year’s report.
If the world wants to cut emissions quickly and meet the climate goals laid out in the Paris Agreement, clean energy will need to grow even faster each year through 2040 than it did during 2017 and 2018.
A 100% Clean Energy Grid Is Emerging
Four nations can already boast that they are now at, or very close to, 100% clean renewable power. Those countries are Iceland (100%), Paraguay (100%), Costa Rica (99%), Norway (98.5%). Right behind them are Austria (at 80%) and Brazil (75%). The main sources of renewable energy for these countries are wind, solar, geothermal, and hydropower.
Other nations are racing to catch up. A new international report lists large population regions “at or above 100%” including Germany’s Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and Schleswig-Holstein regions; New Zealand’s South Island; and Denmark’s Samsø island. In Canada, both Quebec and British Columbia are at nearly 100% renewable power.
In 2018 China’s Xinhua News Agency reported on a test in Qinghai Province that ran for seven days and used only renewable energy, meaning only wind, solar and hydro. This was a demonstration by the Chinese State Grid Corporation to show that a clean energy future is now possible.
Public Transportation For Cities Of The Future
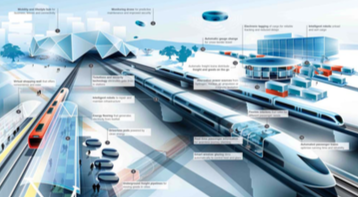
Major urban areas are in the midst of rapid population growth. According to Siemens’ magazine, by 2050 over 75% of the world’s population will live in cities. This will lead to megacities that will be home to 10 million people or more.
A report from the London engineering firm Arup Ltd. highlights the need for future cities to design new rail lines or modernize existing rail systems. In these metropolises, rail will be the primary method of transportation.
With rising global temperatures, an increase and intensity of extreme weather is expected. Changes in temperature, storm activity, and sea level will impact transportation infrastructure, and lead to disruptions and failures in older transportation systems. Future rail systems will have to be built, keeping rising sea levels and climate changes in mind.
The method of powering rail systems must be transformed. According to Railway-Technology.com, an alternate mode of energy is hydrogen-based fuel. “Hydrail” could replace diesel engines and generators. The energy would be from hydrogen fuel cells with electricity stored in batteries from regenerative braking. The hydrogen itself could be mass produced by either wind, solar, or hydroelectric energy production.
Solar Paneled Roads Are Emerging

France has opened a solar panel road in a rural Normandy village. At present this new concept only runs for a short 1 kilometer (0.6-mile) along a test route near the small village of Tourouvre-au-Perche. This was inaugurated in 2018 by France’s ecology minister, Ségolène Royal.
In 2014, a solar-powered bicycle path opened in Krommenie in the Netherlands. Despite a few technical problems, it already generates 3,000 kWh of energy, enough to power an average family home for a year.
China is also developing roads paved with solar panels. The surface of these panels is made of a complex polymer that resembles plastic and contains slightly more friction than a conventional road surface, according to Zhang Hongchao, an engineering professor at Tong-ji University in Shanghai.
Solar roads are part of China’s massive effort to switch rapidly over to solar and wind energy power. At the present time, solar roads are still more expensive than asphalt, but the potential for future benefits are huge. As electric cars become more common, the future could well be free power from solar freeways. (At right, a heavy truck drives on a solar road in Jinan, China).
Silvopasture: Mixing Forests With Animals

Silvopasture is an ancient practice that integrates trees and pasture into a single system for raising livestock. Research shows that silvopasture far outpaces any grassland technique for counteracting the methane emissions of livestock and sequestering carbon under-hoof. Pastures crisscrossed with trees sequester five to ten times as much carbon as those of the same size that are treeless, storing it in both biomass and soil.
Farmers and ranchers benefit from silvopasture. Livestock, trees, and orchard products, such as nuts, fruit, and mushrooms, generate income at different times during the year. The health and productivity of animals and the land improve. It offers more water retention, more biodiversity and less erosion. More birds are present which helps to control insects. There are also more microbiota creating healthier soil, plus it produces more income for the farmer.
Silvopasture runs counter to farming norms and can be costly and slow to implement. It’s being advanced by agroforestry associations around the world. As the impacts of global warming progress, silvopasture can help farmers and livestock adapt to erratic weather and increased drought. Silvopasture averts and sequesters emissions, while protecting against changes that are now inevitable.
Eat Less Red Meat

Animal agriculture is a major cause of greenhouse gases, in part because of the methane produced by the animals, but also because of the massive slurry pits that accompany farms. It also diverts water and grains to animal-rearing, which is less efficient than directing grains towards direct human consumption.
Growing food for the world’s burgeoning population is likely to send greenhouse gas emissions over the threshold of safety unless more is done to cut meat consumption, says a report led by scientists at the Oxford Martin School. They find that shifting to a largely vegetarian diet, or even simply cutting down meat consumption to within accepted health standards, would make a large dent in greenhouse gases.
“Such a step would save lives,” said Dr. Marco Springmann, lead author of another study, entitled “Analysis and valuation of the health and climate change co-benefits of dietary change,” published in a May, 2016 edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“Imbalanced diets, such as diets low in fruits and vegetables and high in red and processed meat, are responsible for the greatest health burden globally in most regions,” he said. “At the same time, the food system is responsible [currently] for more than a quarter of all greenhouse gas emissions.
Phase Out Internal Combustion Engines
The internal combustion engine is facing a huge watershed moment – major auto manufacturer Volvo is scheduled to stop producing petroleum-powered vehicles by 2021, and countries across Europe, including the UK, have vowed to ban their sale before the year 2040.
In Germany, a ban on internal combustion engines is expected to have an impact on the direction of the auto industry. Germany has the fourth largest auto manufacturing industry in the world. Reuters notes a move toward electric vehicles (EVs) would remove many auto repair jobs, since EV powertrains need much less maintenance than combustion engines.
“If the Paris agreement to curb climate-warming emissions is to be taken seriously, no new combustion engine cars should be allowed on the road after 2030,” said German lawmaker Oliver Krischer to Der Spiegel magazine.
This move towards EVs will certainly help mitigate the effects of climate change, especially as the time for more drastic measures is fast approaching. This year’s temperatures are likely to be 1.25o C above pre-industrial times and have already reached levels similar to when Earth’s seas were 20 to 30 feet higher.
A paper by NASA scientist Dr. James Hansen suggests we must do even more if we expect to restrain the rise of temperatures to within 2o C.
Demand Fossil Fuel-Free Cities

“The Climate Crisis Is Already Here,” shouted college students. When the U.S. Mayors convened in Boston in June, 2018, rallies demanded “Fossil Fuel-Free Cities.” This is possible now. Students also emphasized, “Delaying climate action costs human lives.”
In the photo above, students took to the streets of Boston and demanded that mayors and local leaders “walk the talk” on climate and commit to bold action rather than catering to the fossil fuel industry.
In addition to rallies, over a dozen kayaktivists coordinated in the Boston harbor that week and requested a total ban on fracking.
“Growing our dependence on fracked gas further delays the transition to renewables and energy efficiency we need,” declared Alan Palm, an organizer with the group 350.org Massachusetts and the Better Future Project.
This is not a far fetched idea. Over 70 cities and 9 counties across the U.S. have already adopted ordinances setting targets to dramatically overhaul their electricity use, up from 36 cities one year ago. The new total represents at least 10.3 million people using 2.5% of the country’s power output.
An Earth Healing Ethic Of The Environment

Across the State of North Carolina the most recent census showed that 83% of citizens self-identified as a person of faith. What is not widely recognized is that every major religious organization has an ethic of the environment even though it may not always be succinctly stated. In the spirit of the world’s Scriptures, this ethic can be succinctly summarized as follows:
The Earth is the Lord’s and all that is in it; You shall not despoil the earth nor destroy the life on it.
This ethic addresses every environmental issue and embraces virtually all of the world’s faith traditions. For Christians, plus Jews, Muslims and Hindus as well as Indigenous faiths, this implies that every creature and everything on earth has intrinsic sacred value and nothing may be used or done that causes hurt or harm to the earth.
For climate change, this ethic means fossils fuels are a wrong choice and must be replaced by clean, renewable and benevolent forms of energy.
Debunk The Climate Deniers
Former Alaska Governor Sarah Palin once said, “Climate change is hysteria and a lot of junk science” (Source: Wiki-Media Commons). How can a person most effectively deal with those who maintain this sort of misinformation?
To begin, know that all of the peer-reviewed climate science is strong, solid and clear. But science alone is not always enough for some people.
Begin to engage those who do not yet understand climate science by respecting them. Don’t just blurt out what you believe which is mostly a way to start a fruitless argument. Instead, find out what a person thinks is important. Draw deniers out with questions. Different approaches will fit different people. Identify the values of a person, then find ways to build bridges. Don’t make the mistake of thinking that because someone has a
different background, you can’t communicate or that
person can’t change. And don’t turn a denier into an
enemy. You can’t convince everyone. But keep the
conversation alive. Provide information and news
reports. Keep the lines of communication open. Over
time people can and will change.
Slow Down Population Growth

World population is presently growing at a rate of 1.1% per year. Some analysts project that population growth could hit 9 billion by 2050. This is roughly the equivalent of another China plus a large portion of India’s population.
When a country becomes overpopulated, its rate of saving drops; there is less investment in infrastructure; and housing and education problems emerge. Resources become insufficient and unemployment rises. Special measures have to be taken to control the expanding population and maintain order.
The good news is that the world’s growth rate is dropping, from 2.1% in 1962 down to about half that in 2020. A lesson from population growth history is that once a population reaches its carrying capacity, it will stabilize and level off to meet the demands of the environment. Unfortunately this usually occurs after a population has depleted most of its natural resources.
Because population growth includes an increase in carbon emissions, population expansion must be slowed. Worldwatch Institute President Robert Engelman recommends: provide for family planning; educate girls; eradicate gender bias; end policies that reward parents based on family size; integrate lessons on population into schools; convince local leaders of the need to stabilize population; and offer age-appropriate sexuality education for students. If these strategies are applied, Engelman says, world population will decline.
Hydrogen Fuel Cells Are Available

The world’s first commercial hydrogen fuel cell passenger train is now running in northern Germany. Two trains built by the French train maker Alstom are smoothly operating on a 62-mile stretch of track.
This first hydrogen-powered train signals the start of a global effort to replace polluting diesel trains with more eco-friendly technology. Two bright blue Coradia iLint trains are running on a daily route between the cities of Cuxhaven, Bremerhaven, Bremervoerde and Buxtehude, a stretch until June, 2019 that was normally plied by diesel trains.
“This hydrogen powered train system is ready for serial production,” says Alstom CEO Henri Poupart-Lafarge at an unveiling ceremony in Bremervoerde, where the trains will be refueled with hydrogen.
Alstom plans to deliver 14 more of these zero-emissions trains by 2021. Other German states have already expressed an interest as have Britain, Italy, Denmark, Norway and Canada, among others. Hydrogen trains are equipped with fuel cells that produce electricity through a combination of hydrogen and oxygen, a process that leaves steam and water as the only emissions. The Coradia iLint trains run about 600 miles (1,000 km) on a single tank of hydrogen, similar to the range of diesel fueled trains, but at less cost.
Put A Price On Carbon Fuels

A carbon price is a fee applied to fossil fuel pollution to encourage polluters to reduce the amount of greenhouse gas they emit into the atmosphere. There is wide agreement among economists that a carbon fee (or price) is the most effective way for countries to reduce oil, gas and coal emissions.
A carbon price works in two ways. It encourages less use of fossil fuels, but it allows solar and wind power to become sound economic choices. With a carbon price, the costs of slowing climate change are distributed across generations rather than being borne overwhelmingly by future generations.
A carbon fee can be levied by government on the distribution, sale or use of fossil fuels, based on their carbon content. This increases the cost of those fuels and the goods or services created with them, encouraging business and individuals to switch to greener production and consumption. In most plans the government decides how to use this revenue. In one version, called “the fee and dividend” proposal, the revenues are distributed back to the population.
To function properly, the carbon price must be set sufficiently high to encourage polluters to change behavior and reduce pollution.
End The Silence Around Climate Change
Americans rarely talk about climate change, and they too seldom learn about it through the media. This is what a major new survey finds.
That silence reinforces the dangerously wrong notion that climate change isn’t a critical threat requiring urgent action now. And that’s why this is one of the most crucial messaging lessons the climate movement can learn, the need to initiate more conversations about an uncomfortable subject.
Only one in five Americans say they hear people discussing climate change “at least once a month,” according to a 2018 survey by Yale University Center for Climate Communication. Nearly two-thirds of Americans (65%) report they “rarely” or “never” discuss global warming with friends or family.
To change the climate conversation, start talking about climate change. Yes, it’s important to reduce your carbon footprint. And yes, it’s vital to vote for candidates who support climate action. But don’t forget to talk about climate change with friends, family, and even strangers. Until the silence around climate change ends, climate science and solutions will not win the day.